Currency
January 23, 2022
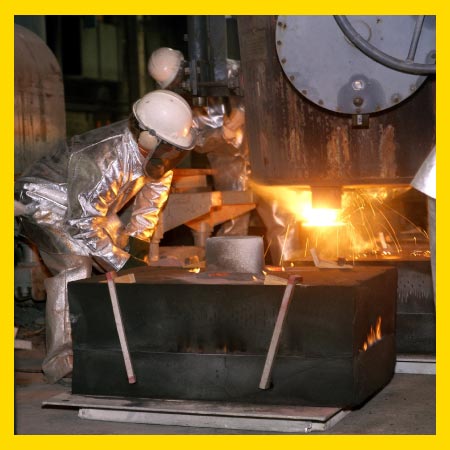

The works of heavy industries involves many vital risks that adversely affect human health. In order to remove or minimize these risks, protective clothings and accessories with the latest technology, tested and certified according to the most up-to-date standards and proven to be reliable, should be preferred. These accessories include eye / face, head, hand and foot protectors. However, in this article, we will mention about special body protection suits against molten metal splashes which are necessary to be used in metal casting factories.
Molten metal splash or explosion of molten metal in the hot furnace is usually caused by the damp, wet, cold or air inside the part thrown into the furnace, and causes the metal to explode violently and dangerous molten metals to spread into the air. These molten metals are very dangerous particles that can reach temperatures up to 1800 °C.
In case of such accidents, these dangerous particles can ignite ordinary workers’ clothes, cause serious injuries by puncturing the clothes, or even cause accidents that result in death. In order to be protected against these very hot splashes, protective clothings with CE marking that are tested according to the relevant standards, successfully passed the tests and certified in accordance with the latest published (EU) 2016/425 PPE Regulation (EU Type Examination Certificate) that replaced the old 89/686/EEC Personal Protective Equipment Directive should be used.
Let’s mention about the European Standards that this type of protective clothings must have.
General purpose industrial heat and flame resistant suits are produced in accordance with EN ISO 11612:2015 standard, with options such as anti-static properties, and are designed and certified for every need of the user.
Protective clothing against molten metal splashes in the content of this standard, whose performance is defined (the table explaining performance levels is given in my article), provides protection against molten aluminum, iron, steel, copper and other similar molten metal splashes. The clothing should allow those who deal with hot metals to work comfortably in their daily work without sacrificing comfort. In addition to daily work, the user must act very quickly in special situations and accidents. It should be designed in such a way that it allows rapid movement with comfort. These clothings can be produced in a single layer or multi-layered according to need.
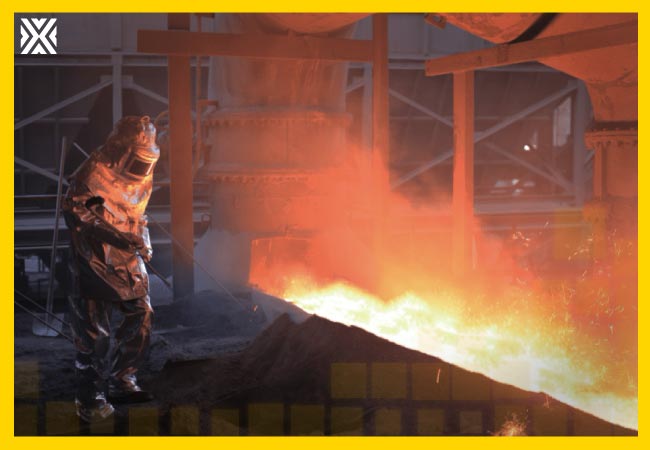

Important: The most recent version of the EN ISO 11612 standard is 2015. 2008 and 2010 versions are no longer in use. It is important to pay attention to this point when choosing a protective clothing.
In addition, the fact that only the protective suit’s fabric is certified or having test reports are not sufficient for the safe use of the protective suit. In accordance with the PPE Regulation in most countries, it is obligatory for the finished protective clothing to have CE marking on it as in every personal protective equipment. It is not correct to use a PPE if only the fabric constituting the product is certified, the finished product does not have the EU Type examination certificate according to the most up-to-date EN standards, and the product is supplied and used without CE mark and without label.
Heat and flame resistant clothing used to safely complete welding works must be certified according to EN ISO 11611:2015 standard. Class 1 according to this standard provides protection for less dangerous welding techniques and situations that cause low level splash and radiant heat. Class 2 means that it provides protection for more dangerous welding techniques and situations that cause higher levels of splash and radiant heat.
Important: The most current version of the EN ISO 11611 standard is 2015. 2007 version is no longer in use. This should be considered in the selection of a protective clothing.
EN 1149-3/5:2008 standard is used to minimize the risk of accident that may occur due to electrostatic discharge that may cause fire or explosion in environments where explosive substances may be present, and thanks to the anti-static fiber contained in the fabric of a protective suit, it is called anti-static suit.
Important: This standard does not imply protection against voltage or electric shock. Due to the feedback received from users from time to time, the obligation to provide this information has arisen.
EN ISO 13688:2013
Standard replaces the old EN 340:2004 standard and expresses general performance requirements for ergonomics for protective clothing, the use of substances that do not harm human health, the indication of sizes, wearing and compatibility information that must be marked and specified by the manufacturer on the clothing. This standard is used in conjunction with the other standards mentioned above that contain requirements for specific performances.
In order to classify the protective clothings according to the EN ISO 11612:2015 standard and to decide whether the suit is suitable to work with molten metals, the results of the tests given in the table below are considered as criteria. These test methods are referenced by the standards required for certification.